Single-shot powder X-ray diffraction in pulsed high magnetic fields using a portable single-turn-coil system
To investigate the states of materials in detail, physical ddproperty measurements using
microscopic probes are indispensable. Although microscopic measurements under the pulsed
ultrahigh magnetic fields are highly challenging, they are essential for advancing high
magnetic-field science. Recently, Ikeda group (the University of Electro-Communications) has
developed a single-shot X-ray diffraction (XRD) at SACLA by combining an X-ray free-electron
laser with the portable pulsed high-field generator PINK-02. CUrrently, powder XRD experiments
up to 110 T down to 5 K are available [A].
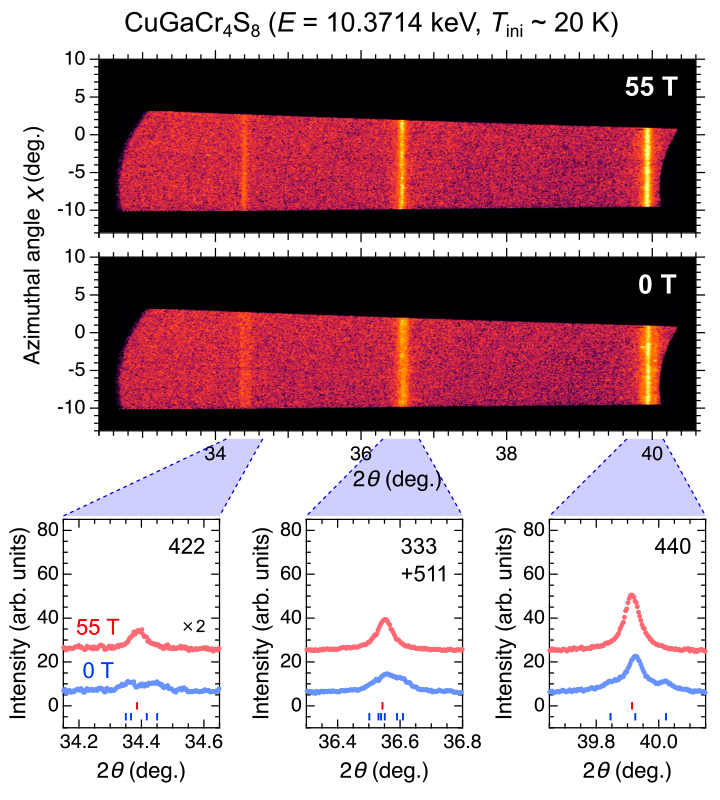
Using this technique, we investigated changes in lattice symmetry across the field-induced phase transition of the breathing-pyrochlore magnet CuGaCr4S8. CuGaCr4S8 undergoes a structural transition below 31 K, developing an orthorhombic distortion and an incommensurate helical magnetic order [B]. Upon applying a magnetic field, a metamagnetic transition occurs at 40 T, followed by a 1/2 magnetization plateau [C]. Focusing on this plateau phase, we performed powder XRD under pulsed fields up to 55 T. We observed that XRD peaks split at zero field coalesce into single, sharp peaks at high fields [D]. This behavior indicates that the lattice symmetry in the plateau phase is cubic, consistent with expectations for a 3-up-1-down magnetic structure.
[B] M. Gen et al., J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 93, 104602 (2024). (Original paper [29])
[C] M. Gen et al., Phys. Rev. Mater. 7, 104404 (2023). (Original paper [24])
[D] M. Gen et al., Phys. Rev. B 111, 214441 (2025). (Original paper [36])
Using this technique, we investigated changes in lattice symmetry across the field-induced phase transition of the breathing-pyrochlore magnet CuGaCr4S8. CuGaCr4S8 undergoes a structural transition below 31 K, developing an orthorhombic distortion and an incommensurate helical magnetic order [B]. Upon applying a magnetic field, a metamagnetic transition occurs at 40 T, followed by a 1/2 magnetization plateau [C]. Focusing on this plateau phase, we performed powder XRD under pulsed fields up to 55 T. We observed that XRD peaks split at zero field coalesce into single, sharp peaks at high fields [D]. This behavior indicates that the lattice symmetry in the plateau phase is cubic, consistent with expectations for a 3-up-1-down magnetic structure.
References
[A] A. Ikeda, M. Gen et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. in press. [arXiv:2504.10085][B] M. Gen et al., J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 93, 104602 (2024). (Original paper [29])
[C] M. Gen et al., Phys. Rev. Mater. 7, 104404 (2023). (Original paper [24])
[D] M. Gen et al., Phys. Rev. B 111, 214441 (2025). (Original paper [36])